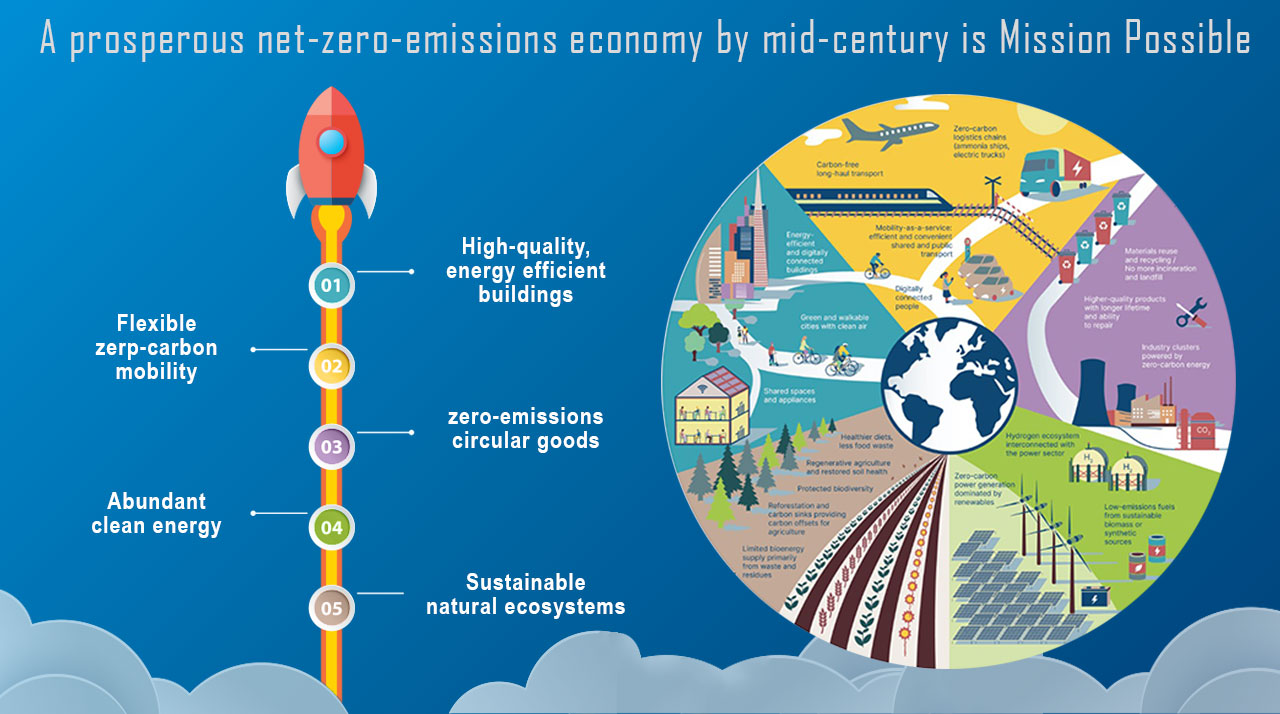
What is net zero?
As the world becomes more conscious of climate change and its impact, more organizations are committing to reducing their carbon footprint and achieving Net Zero emissions. At Sol Partners, we’re committed to helping businesses reach their Net Zero goals through a variety of innovative solutions.
Our team of experts can help you assess your organization’s current carbon emissions and develop a plan to reduce your footprint. We’ll work with you to identify areas where you can improve energy efficiency, adopt renewable energy sources, and implement energy storage solutions. We’ll also help you measure your progress and adjust your plan as needed to ensure you reach your Net Zero goals.
In addition, we can help you leverage renewable energy certificates (RECs) and carbon offsets to achieve Net Zero. Our RECs allow you to purchase renewable energy that matches your organization’s energy consumption, reducing your reliance on fossil fuels. Carbon offsets enable you to invest in projects that reduce carbon emissions, such as renewable energy or energy efficiency projects, to offset the emissions your organization produces.
Investing in Net Zero solutions can not only help you meet your sustainability goals, but it can also improve your brand reputation and create opportunities for cost savings. At Sol Partners, we’re here to help you achieve your Net Zero goals and make a positive impact on the environment. Contact us to learn more about our Net Zero solutions and how we can help your organization become a leader in sustainability.

Why is reaching Net Zero important?
Reaching net zero is important because it is a critical step towards addressing the urgent and ongoing global climate crisis. As the Earth's temperature continues to rise due to greenhouse gas emissions, it's becoming increasingly clear that we must rapidly reduce our carbon footprint and transition to a low-carbon economy. This is essential to limit the increase in global temperature and avoid the most severe impacts of climate change, such as more frequent and intense heatwaves, droughts, floods, and rising sea levels.

How can net zero be achieved?
Transitioning to a net-zero world is one of the greatest challenges humankind has faced. It calls for nothing less than a complete transformation of how we produce, consume, and move about. The energy sector is the source of around three-quarters of greenhouse gas emissions today and holds the key to averting the worst effects of climate change. Replacing polluting coal, gas and oilfired power with energy from renewable sources, such as wind or solar, would dramatically reduce carbon emissions
According to the leading GHG Protocol corporate standard, a company’s greenhouse gas emissions are classified into three scopes. Scope 1 and 2 are mandatory to report, whereas scope 3 is voluntary and the hardest to monitor. However, companies succeeding in reporting all three scopes will gain a sustainable competitive advantage
Then, mobile combustion is all vehicles owned or controlled by a firm, burning fuel (e.g. cars, vans, trucks). The increasing use of “electric” vehicles (EVs), means that some of the organization fleets could fall into Scope 2 emissions

Scope 1 emissions Scope 2 emissions are indirect emissions from the generation of purchased energy, from a utility provider. In other words, all GHG emissions released in the atmosphere, from the consumption of purchased electricity, steam, heat and cooling

Read this paragraph carefully as scope 3 emissions represent the holy grail of emissions. Scope 3 emissions are all indirect emissions – not included in scope 2 – that occur in the value chain of the reporting company, including both upstream and downstream emissions. In other words, emissions are linked to the company’s operations. According to GHG protocol, scope 3 emissions are separated into 15 categories

We offer a range of services to help you measure and manage your value and supply chain emissions:
Value and supply chain sustainability
Includes building a low carbon strategy and supplier engagement. Up to 90% of an organization's environmental impact lies in the value chain - either upstream (supply chain) or downstream eg product use phase. Analyzing and taking action on your value chain is therefore a vital step for any business that wants to become more sustainable and prepare for a low carbon economy
Footprint measurement and analysis
Includes calculation of your organization or product carbon footprint. This provides the baseline needed to implement an effective sustainability and carbon reduction strategy. It can help you identify waste, reduce costs, boost sales and enhance your brand. We can help measure emissions under your direct control (Scope 1 and 2) as well as your organization's indirect emissions (Scope 3)

- +65-88009906
- +65-90445114
-
625 Aljunied road, 05-06,
Aljunied Industrial Complex,
Singapore, 389836
©2022 SOLPTN, All Rights Reserved.




















